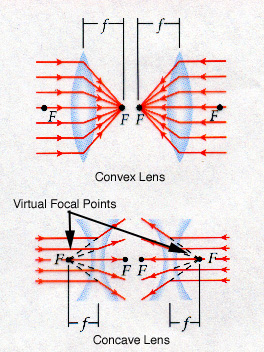

Lenses differ from mirror in one fundament area. Mirrors reflect and lenses refract. Because lenses are light transmitters, the ray diagrams must show light passing through rather than reflecting off. As is shown in the illustration above, light traveling parallel to the principle axis toward a convex lense will converge to a point called the focal point (F), and light that travels parallel to the principle axis toward a concave lens diverges away from a virtual focal point.
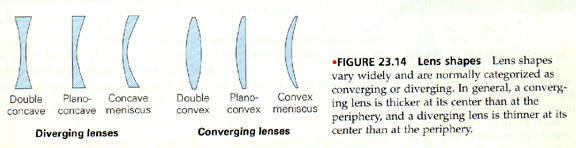
The image displayed below describes the types of lenses that are used in everyday applications. It is important to note that the images produced by these lenses do not depend on what side of the lens the object is on. (In other words, the lenses are completely reversible.)
Convex lenses converge light thus behaving similarly to a concave mirror. The drawings displayed below depict the various cases for convex (converging) lenses. The explanation of the three rays used to create these diagrams can be found below.
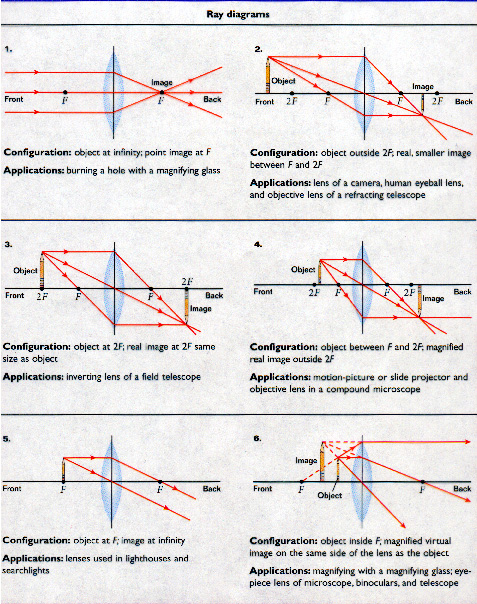
Light that travels into a convex lens parallel to the principle axis refracts out through the back F.
Light that travels in from front F refracts out parallel to the principle axis.
Light that travels into the center of the lens does not bend.
As was true for mirrors, ray diagrams for lenses provide information on the following for image characteristics:
Location
Orientation - erect or inverted
Magnification - magnified or reduced
Image Type - real or virtual
Note that parallels can be drawn between the cases described for concave mirrors and the ray diagrams shown above for convex lenses.
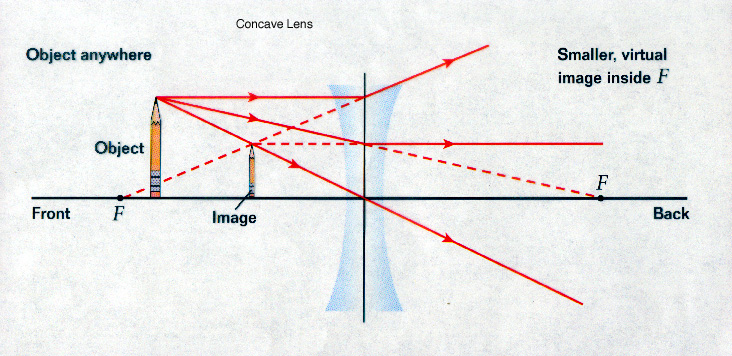
Ray 1: Light that travels into a concave lens parallel to the principle axis refracts out away from the front F.
Ray 2: Light that travels into a concave lens toward the back F refracts out parallel.
Ray 3: Light that travels into the center of a concave lens experiences no bend.
Note that as was shown for convex mirrors, a concave lenses produces only one type of image.