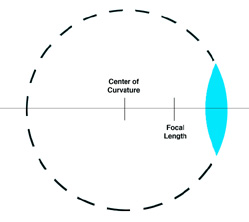
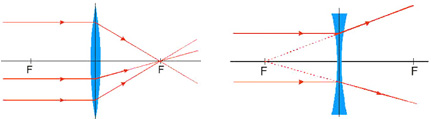
The focal length of the lens is determined by the amount of curvature of the lens. If the lens were made into a spherical piece of glass, the center of curvature of the lens is the point which would be the center of the sphere. The focal point is half of the center of curvature, so the larger the center of curvature, the larger the focal length.